Understanding Ultrasound Imaging
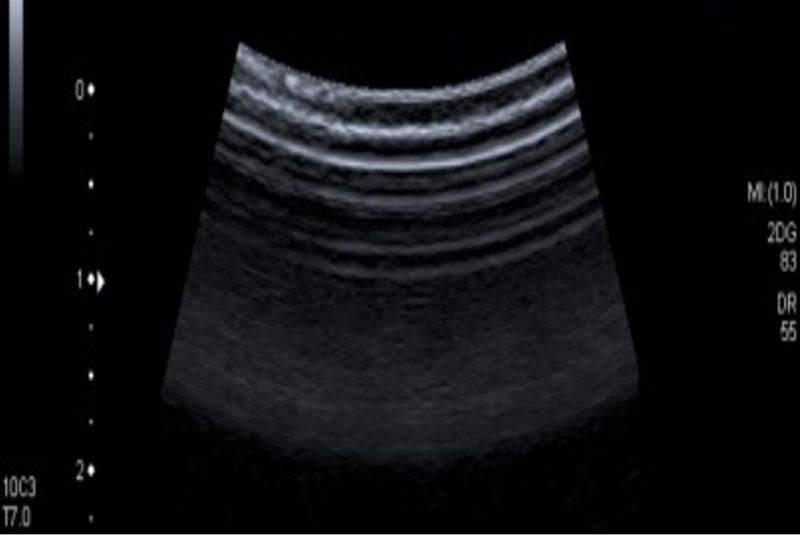
Ultrasound imaging is a common tool in hospitals used to create pictures of the inside of a patient’s body. It’s often used for examining unborn babies in pregnant women and diagnosing various conditions. An ultrasound machine sends high-frequency sound waves into the body, and these waves bounce back from different tissues. The machine then uses these echoes to create real-time images.
Why is modelling an ultrasound transducer challenging?
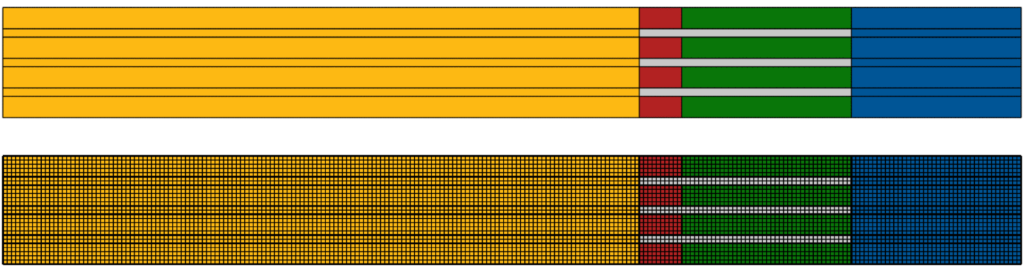
Designing an ultrasound device is complex. These devices use tiny crystals that vibrate to send and receive sound waves. The setup includes:
- Piezoelectric Crystals (red): These generate and detect sound waves.
- Backing Material (yellow): This supports the crystals.
- Acoustic Matching Layer (green): This helps sound waves travel efficiently.
- Lens (blue): This focuses the sound waves.
Creating a computer model of an ultrasound device involves simulating electrical signals, sound wave movements, and how the waves turn back into electrical signals. This is a multiphysics problem, meaning it involves multiple areas of physics.
How can we simplify the problem?
To make the problem more manageable, engineers use various techniques:
- Symmetry: Using symmetrical properties to reduce the complexity.
- Simpler Maths: Using easier mathematical formulas when possible.
- Truncation: Cutting down the size of the model while maintaining accuracy.
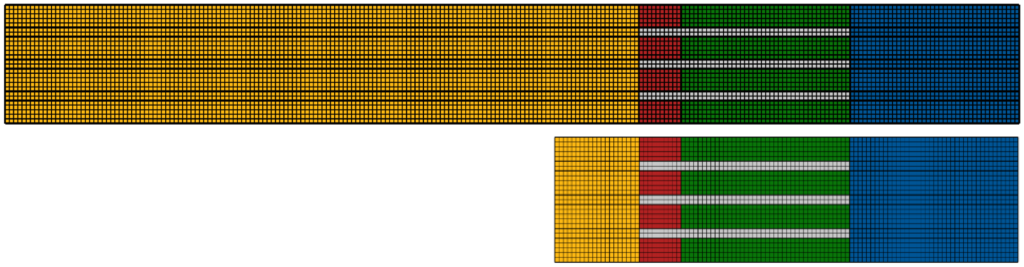
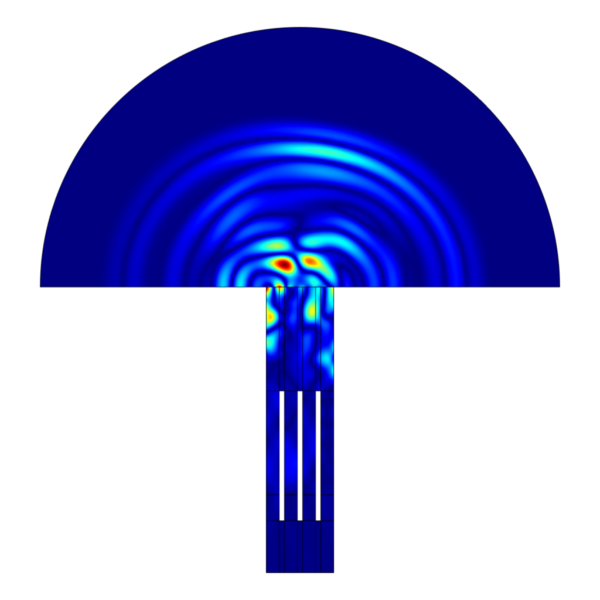
For instance, in a beam-steered transducer (which directs sound waves in specific directions), using simpler formulas might miss important details. Instead, engineers might cut down the size of the model, applying a special boundary that absorbs sound waves to avoid reflections, thereby simulating a larger area.
Results
By cutting the model and using absorbing boundaries, the simulation still accurately shows how sound waves behave but requires less computing power and time. Here’s a bit more detail on the results:
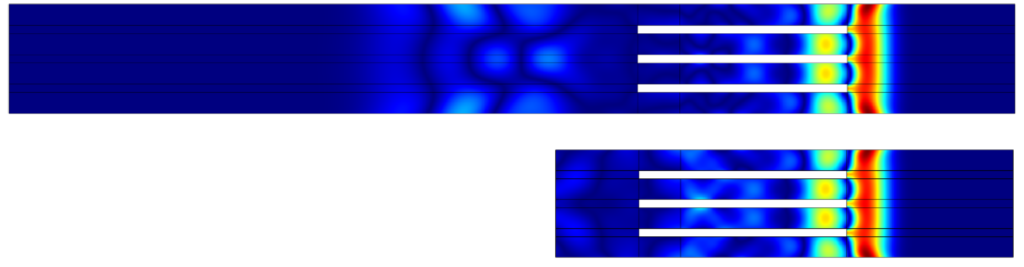
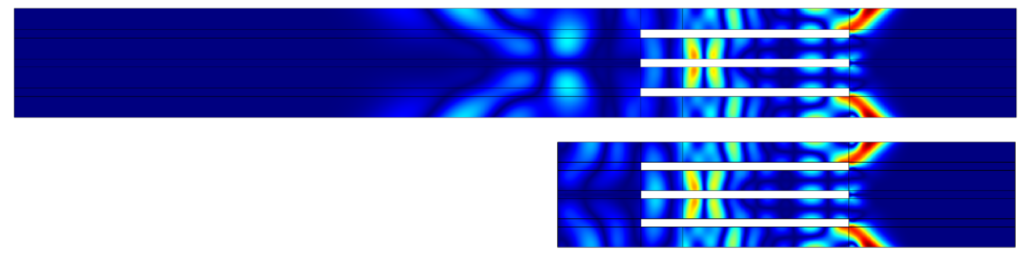
- Pressure and Shear Waves: In both full and truncated models, the waves generated by the crystals travel through the device. The full model shows these waves being absorbed by the backing material, which is what we expect. The truncated model, which is simplified, shows similar behaviour, meaning it still works well.
- Solving Time: Using the truncated model, the solving time is cut in half—from 10 minutes to less than 5 minutes. This time saving is significant, especially when working with complex transducer arrays with many elements.
- Efficiency with Additional Elements: When additional elements are added to the model (up to 128), the solving time remains efficient. Even with an acoustic target volume, the solve time only increases to about 7.5 minutes, which is still manageable.
Other Techniques to Consider
For very large models, especially in 3D, traditional solid mechanics might be too complicated. In such cases, simpler approaches using acoustic or elastic wave models can be more practical.
What We Used to Make These Models
The simulations mentioned used software called COMSOL Multiphysics, involving:
- Electrostatics
- Solid Mechanics
- Acoustics
Why choose Xi for your next project
Our engineering team at Xi has extensive experience in various industries, from designing headphones to studying vibrations from wind turbines. The techniques we discussed can be applied to many fields, including designing speakers, microphones, and analysing ground vibrations.
By using these advanced modelling techniques, we help create accurate and efficient designs, saving time and resources while ensuring high-quality results.